 Induction Sealing Guide
Induction Sealing Guide
Have you ever wondered what induction sealing is and how to use it for your product line? Take a look at our informational page to learn more about the process and benefits of using an induction sealing system.
Induction Sealing: What Is It?
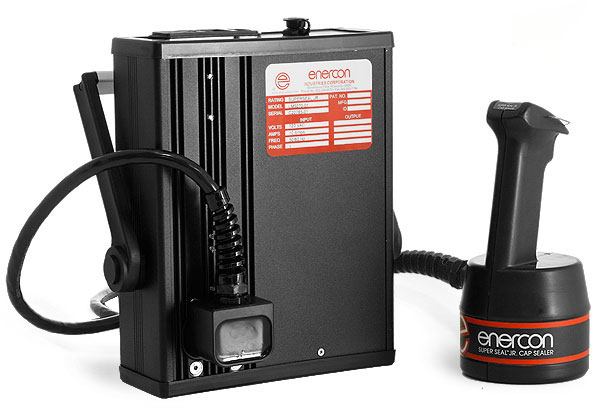
The induction sealing process bonds a foil laminate inner seal to the lip of a container. After the container has been filled and capped with an induction-lined closure, it passes underneath the induction sealing system. The non-contact heating process welds the liner to the container creating a hermetic seal. The FDA regards induction sealing to be an effective method of tamper evidence
When properly applied, induction lined caps provide a hermetic, leak proof, and tamper evident seal. Using an induction sealing system is ideal for extending product shelf life, preserving freshness, preventing costly leaks and enhancing your product's value.
When properly applied, induction lined caps provide a hermetic, leak proof, and tamper evident seal. Using an induction sealing system is ideal for extending product shelf life, preserving freshness, preventing costly leaks and enhancing your product's value.

How Induction Sealing Works
An induction sealing machine features two standard components: the power supply and sealing head. The sealing head consists of a coiled conductor covered by plastic housing. When the power supply energizes the inductive coil, it produces an electro magnetic current, called an eddy current. When a container fitted with an induction lined cap passes through this current, the foil from the inner-seal is heated. This melts the foil's outer polymer coating, which forms a bond with the lip of the container.
Choosing the Right Container, Cap & Liner Materials
Selecting the best induction liner for your product is dependent on several factors, such as the container's material and application.
Induction liners are available in one-piece or two-piece construction. The one-piece type consists of a foam-backed or paper-backed foil laminate. After the sealing process, the entire liner will be completely removed from the cap.
A two-piece liner has an additional wax layer and pulp board layer. The induction heating process will melt the wax, which is absorbed into the pulp board, releasing it from the foil liner. The pulp board layer remains inside the cap for improved resealing after the foil liner has been removed.
Plastic containers with continuous thread plastic caps produce the most consistent seal with the least challenges. Some glass containers may need to be treated in order to properly accept an induction seal. Sealing with metal caps is possible, but can pose several problems. As the induction system heats the foil liner, it also heats the metal cap, which can remain hot for a while. This can become a safety hazard and could also melt the threads if used on plastic containers.
Induction liners are available in one-piece or two-piece construction. The one-piece type consists of a foam-backed or paper-backed foil laminate. After the sealing process, the entire liner will be completely removed from the cap.
A two-piece liner has an additional wax layer and pulp board layer. The induction heating process will melt the wax, which is absorbed into the pulp board, releasing it from the foil liner. The pulp board layer remains inside the cap for improved resealing after the foil liner has been removed.
Plastic containers with continuous thread plastic caps produce the most consistent seal with the least challenges. Some glass containers may need to be treated in order to properly accept an induction seal. Sealing with metal caps is possible, but can pose several problems. As the induction system heats the foil liner, it also heats the metal cap, which can remain hot for a while. This can become a safety hazard and could also melt the threads if used on plastic containers.

SKS's stock induction lined cap has a one-piece foam backed liner, which can be used to seal polyethylene (HDPE & LDPE), polystyrene, PET, PVC and glass containers.
>> Purchase Induction Lined Caps
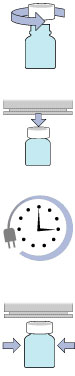
- Caps have been applied with the proper torque
- Creates consistent pressure between circumference of the container lip and liner
- See our Torque Guide for more info
- Adequate distance between the cap and sealing head
- More sealing strength closer to the coil
- Optimal distance is 1/8 inch
- Induction sealer's power setting and amount of sealing time
- Too little heat: weak seal; too much heat: burned or deformed liner
- Begin testing at minimum power; increase by 1-2% with subsequent containers until desired seal is achieved
- Container is properly centered under sealing head
- Ensures liner will bond evenly to container lip
Choosing the right power supply strength will depend on the size of your closure and the speed at which the production line will operate. The sealing head design depends on the application. The two most common designs are a flat sealing head or a tunnel head.
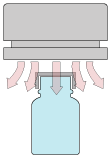
Flat Sealing Head
Widely disperses the electromagnetic field.
Advantages:
- Able to seal a large area
- Accommodates various cap sizes without exchanging sealing head
Disadvantages:
- Less concentrated field can cause in inconsistent seals if container is not properly centered
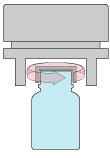
Tunnel Sealing Head
Concentrated magnetic field on sides and above cap.
Advantages:
- Uniform field, which results in a more consistent seal
- Deeper field allows for sealing thicker closures (ex. child resistant caps) or closures with recessed liners (ex. spout caps, push/pull caps)
Disadvantages:
- Cannot accommodate a broad range of neck finishes
Induction Sealing Links & Resources
For more detailed information on induction sealing, read "
Unraveling the Myths & Mysteries of Induction Sealing," written by Bill Zito, VP of Enercon Industries. You may also like to watch our informative
how-to video
illustrating how to use an induction sealing machine.
Chat with Us
Why Businesses Choose SKS Bottle & Packaging
SKS Bottle & Packaging makes it easy to order bottles, jars, and packaging supplies online. From fast shipping to flexible savings programs, our goal is to help businesses of all sizes source reliable packaging with a smooth and efficient ordering experience.






 Shop All Packaging
Shop All Packaging Glass Containers
Glass Containers Plastic Containers
Plastic Containers Metal Containers
Metal Containers Cardboard Containers
Cardboard Containers Industrial Containers
Industrial Containers Caps / Closures
Caps / Closures Shrink Bands
Shrink Bands Design Custom Labels
Design Custom Labels Subscribe & Save Orders
Subscribe & Save Orders Shop By Industry
Shop By Industry Custom Packaging
Custom Packaging Pallet Qty Packaging
Pallet Qty Packaging SKS Direct Wholesale
SKS Direct Wholesale Packaging Equipment
Packaging Equipment Help/Info
Help/Info New Products
New Products Promotions
Promotions Newsletters
Newsletters Combo Kit Deals
Combo Kit Deals Product Closeouts
Product Closeouts Recently Back In Stock
Recently Back In Stock













